Renewable Natural Gas
RNG has dual environmental benefits. First, capturing biogas prevents methane, a greenhouse gas, from being released into the atmosphere and trapping heat. Second, utilizing RNG for electricity generation, as a transportation fuel, in residential and industrial applications, or to produce hydrogen is cleaner than traditional sources.
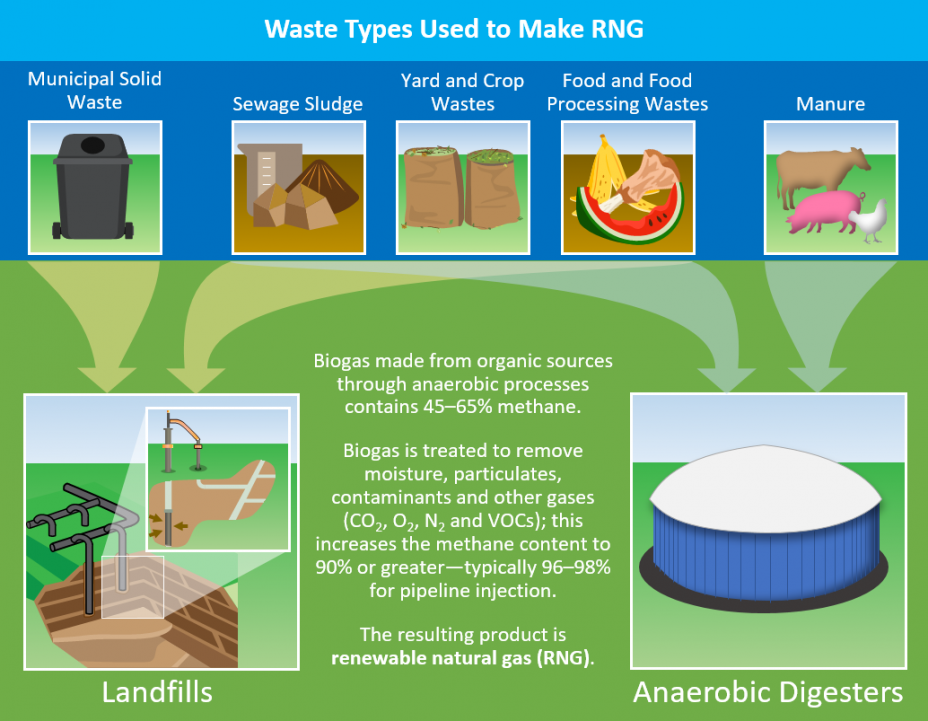
Biogas naturally occurs at sources such as landfills, farms, and wastewater treatment facilities as organic matter decomposes. Left uncaptured, this biogas is a source of methane being emitted to the atmosphere. Instead of being left uncaptured, thus causing an increase in greenhouse gases, methane can be kept out of the atmosphere by the capture of biogas at these types of facilities. The biogas is then cleaned and converted into Renewable Natural Gas (RNG). RNG is simply biogas from organic waste materials that has been cleaned to the quality of conventional natural gas. Since RNG is a direct replacement for conventional natural gas, it can be used in all of the same applications.
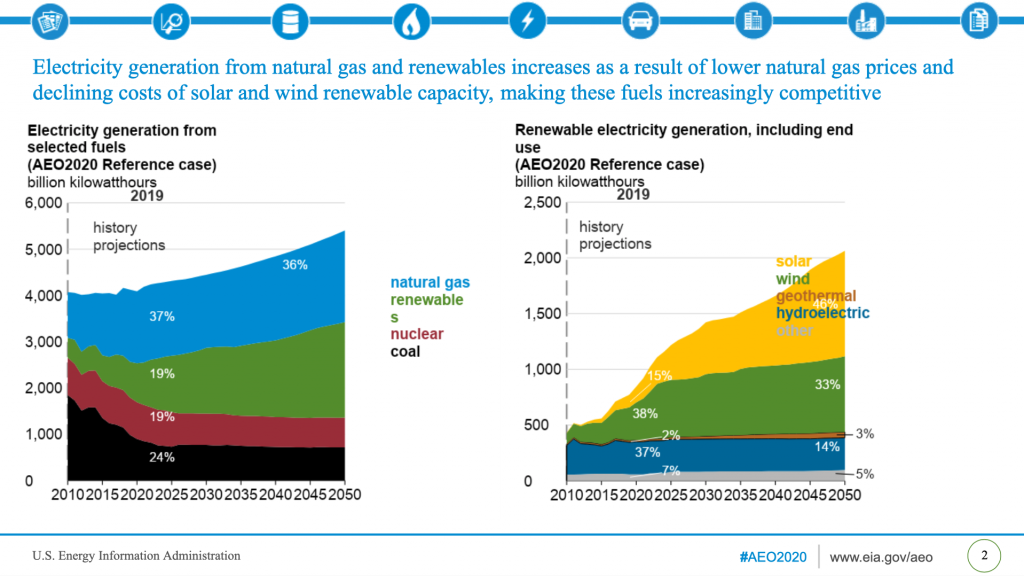
As the Energy Information Administration diagram shows, the renewables sector is anticipated to continue to grow into the future as a source of electricity generation. While coal and nuclear are anticipated to decrease by 2050, natural gas as a source is expected to remain relatively stable. Utilizing available RNG as a source in place of conventional natural gas will offer achievable environmental benefits.